libmdbx
Revised and extended descendant of Symas LMDB.
Project Status
MDBX is under active development, database format and API aren't stable at least until 2018Q2. New version won't be backwards compatible. Main focus of the rework is to provide clear and robust API and new features.
Contents
Overview
libmdbx is an embedded lightweight key-value database engine oriented for performance.
libmdbx allows multiple processes to read and update several key-value tables concurrently, while being ACID-compliant, with minimal overhead and operation cost of Olog(N).
libmdbx provides serializability and consistency of data after crash. Read-write transactions don't block read-only transactions and are serialized by mutex.
libmdbx wait-free provides parallel read transactions without atomic operations or synchronization primitives.
libmdbx uses B+Trees and mmap, doesn't use WAL. This might have caveats for some workloads.
Comparison with other DBs
Because libmdbx is currently overhauled, I think it's better to just link chapter of Comparison with other databases here.
History
libmdbx design is based on Lightning Memory-Mapped Database. Initial development was going in ReOpenLDAP project, about a year later it received separate development effort and in autumn 2015 was isolated to separate project, which was presented at Highload++ 2015 conference.
Since early 2017 libmdbx is used in Fast Positive Tables, by Positive Technologies.
Acknowledgements
Howard Chu (Symas Corporation) - the author of LMDB, from which originated the MDBX in 2015.
Martin Hedenfalk martin@bzero.se - the author of btree.c code,
which was used for begin development of LMDB.
Main features
libmdbx inherits all keys features and characteristics from LMDB:
-
Data is stored in ordered map, keys are always sorted, range lookups are supported.
-
Data is mmaped to memory of each worker DB process, read transactions are zero-copy.
-
Transactions are ACID-compliant, thanks to MVCC and CoW. Writes are strongly serialized and aren't blocked by reads, transactions can't conflict with each other. Reads are guaranteed to get only commited data (relaxing serializability).
-
Reads and queries are non-blocking, don't use atomic operations. Readers don't block each other and aren't blocked by writers. Read performance scales linearly with CPU core count.
Though "connect to DB" (start of first read transaction in thread) and "disconnect from DB" (shutdown or thread termination) requires to acquire a lock to register/unregister current thread from "readers table"
-
Keys with multiple values are stored efficiently without key duplication, sorted by value, including integers (reasonable for secondary indexes).
-
Efficient operation on short fixed length keys, including integer ones.
-
WAF (Write Amplification Factor) и RAF (Read Amplification Factor) are Olog(N).
-
No WAL and transaction journal. In case of a crash no recovery needed. No need for regular maintenance. Backups can be made on the fly on working DB without freezing writers.
-
No custom memory management, all done with standard OS syscalls.
Performance comparison
All benchmarks were done by IOArena and multiple scripts runs on Lenovo Carbon-2 laptop, i7-4600U 2.1 GHz, 8 Gb RAM, SSD SAMSUNG MZNTD512HAGL-000L1 (DXT23L0Q) 512 Gb.
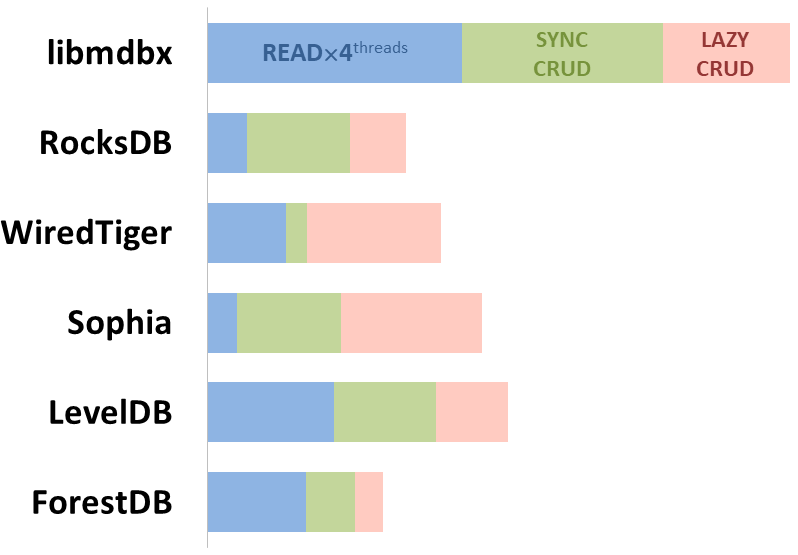
Integral performance
Here showed sum of performance metrics in 3 benchmarks:
-
Read/Search on 4 CPU cores machine;
-
Transactions with CRUD operations in sync-write mode (fdatasync is called after each transaction);
-
Transactions with CRUD operations in lazy-write mode (moment to sync data to persistent storage is decided by OS).
Reasons why asynchronous mode isn't benchmarked here:
-
It doesn't make sense as it has to be done with DB engines, oriented for keeping data in memory e.g. Tarantool, Redis), etc.
-
Performance gap is too high to compare in any meaningful way.
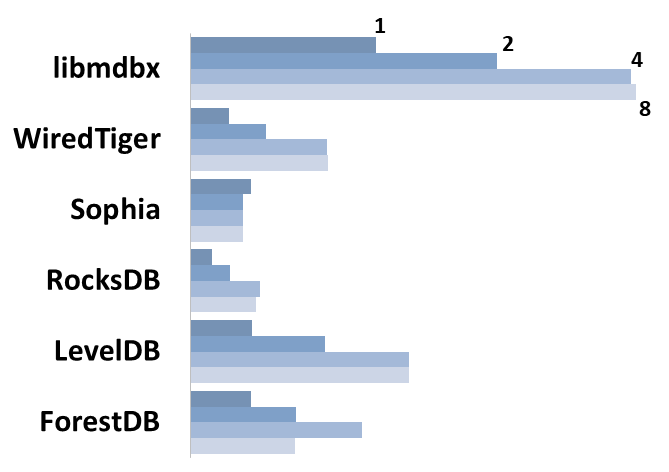
Read Scalability
Summary performance with concurrent read/search queries in 1-2-4-8 threads on 4 CPU cores machine.
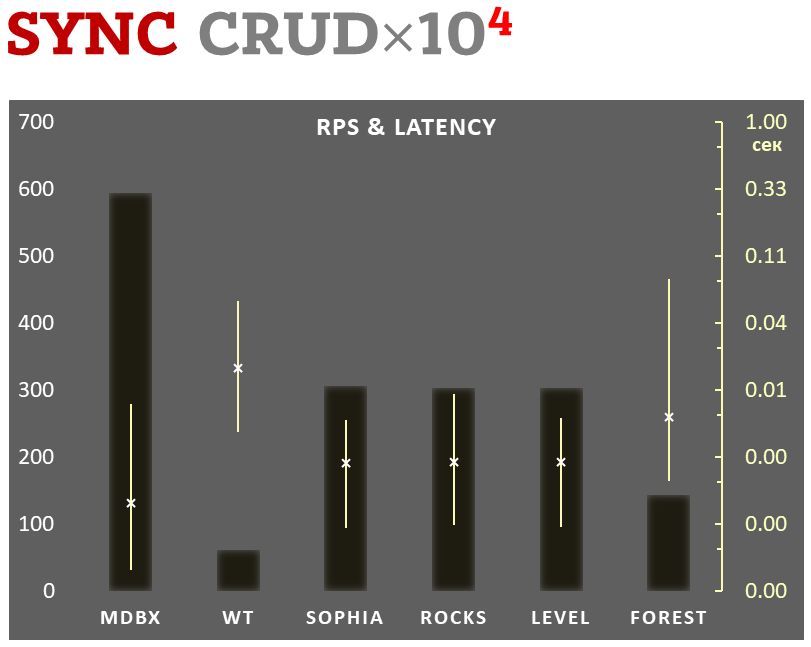
Sync-write mode
-
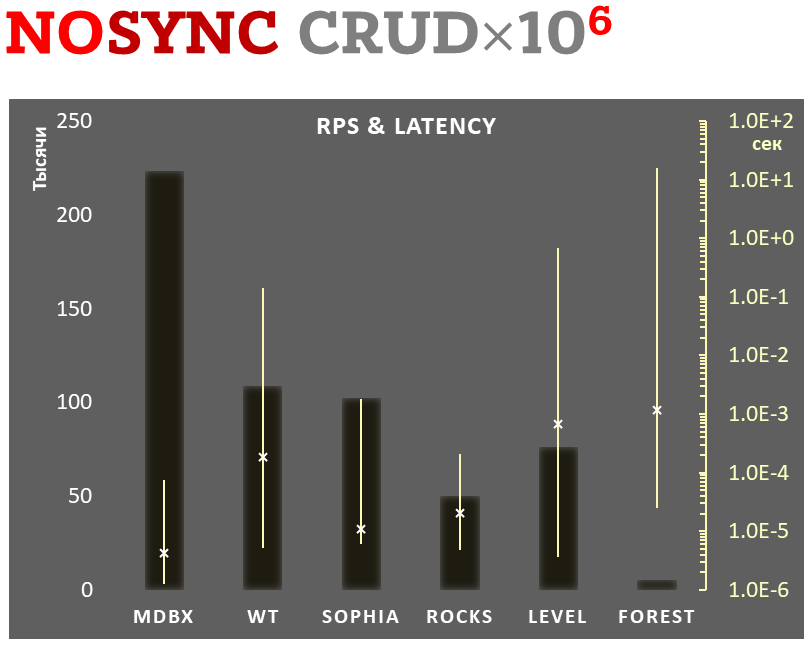
Linear scale on left and dark rectangles mean arithmetic mean transactions per second;
-
Logarithmic scale on right is in seconds and yellow intervals mean execution time of transactions. Each interval shows minimal and maximum execution time, cross marks standard deviation.
10,000 transactions in sync-write mode. In case of a crash all data is consistent and state is right after last successful transaction. fdatasync syscall is used after each write transaction in this mode.
In the benchmark each transaction contains combined CRUD operations (2 inserts, 1 read, 1 update, 1 delete). Benchmark starts on empty database and after full run the database contains 10,000 small key-value records.
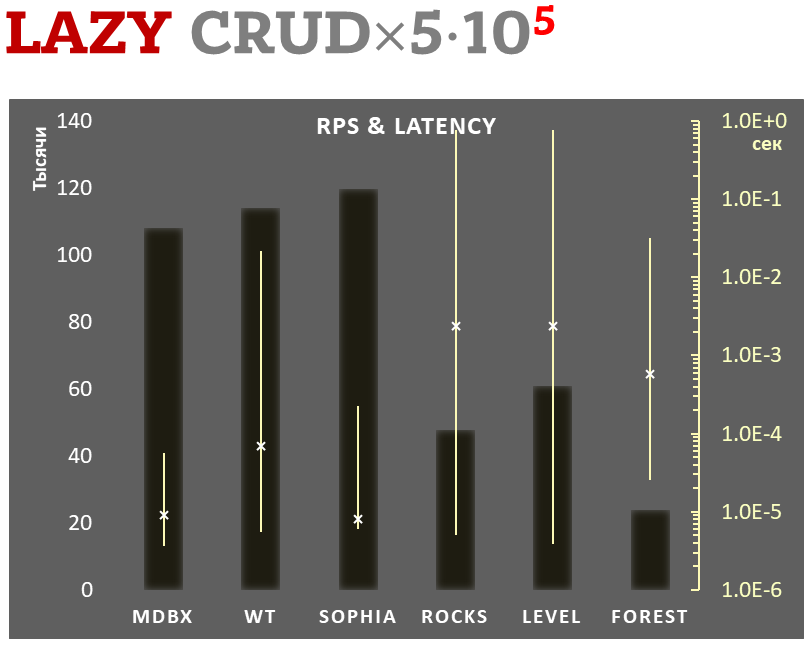
Lazy-write mode
-
Linear scale on left and dark rectangles mean arithmetic mean of thousands transactions per second;
-
Logarithmic scale on right in seconds and yellow intervals mean execution time of transactions. Each interval shows minimal and maximum execution time, cross marks standard deviation.
100,000 transactions in lazy-write mode. In case of a crash all data is consistent and state is right after one of last transactions, but transactions after it will be lost. Other DB engines use WAL or transaction journal for that, which in turn depends on order of operations in journaled filesystem. libmdbx doesn't use WAL and hands I/O operations to filesystem and OS kernel (mmap).
In the benchmark each transaction contains combined CRUD operations (2 inserts, 1 read, 1 update, 1 delete). Benchmark starts on empty database and after full run the database contains 100,000 small key-value records.
Async-write mode
-
Linear scale on left and dark rectangles mean arithmetic mean of thousands transactions per second;
-
Logarithmic scale on right in seconds and yellow intervals mean execution time of transactions. Each interval shows minimal and maximum execution time, cross marks standard deviation.
1,000,000 transactions in async-write mode. In case of a crash all data will be consistent and state will be right after one of last transactions, but lost transaction count is much higher than in lazy-write mode. All DB engines in this mode do as little writes as possible on persistent storage. libmdbx uses msync(MS_ASYNC) in this mode.
In the benchmark each transaction contains combined CRUD operations (2 inserts, 1 read, 1 update, 1 delete). Benchmark starts on empty database and after full run the database contains 10,000 small key-value records.
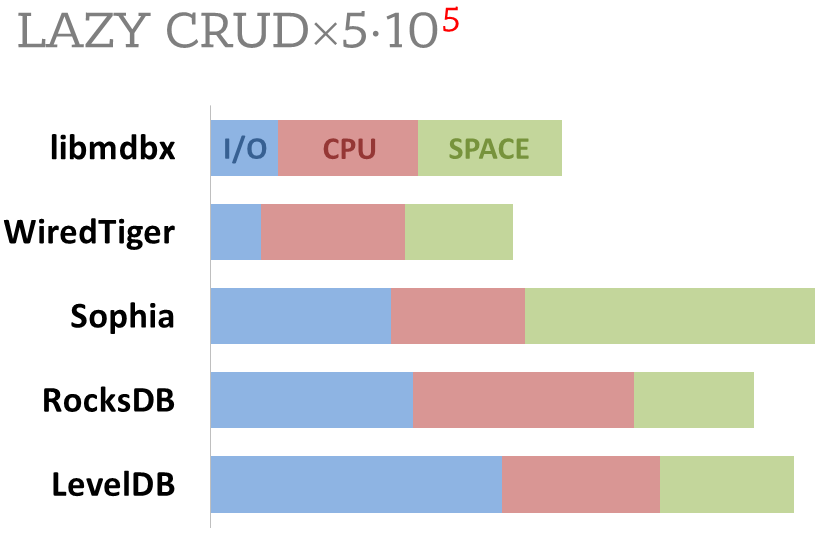
Cost comparison
Summary of used resources during lazy-write mode benchmarks:
-
Read and write IOPS;
-
Sum of user CPU time and sys CPU time;
-
Used space on persistent storage after the test and closed DB, but not waiting for the end of all internal housekeeping operations (LSM compactification, etc).
ForestDB is excluded because benchmark showed it's resource consumption for each resource (CPU, IOPS) much higher than other engines which prevents to meaningfully compare it with them.
All benchmark data is gathered by getrusage() syscall and by scanning data directory.
Gotchas
-
At one moment there can be only one writer. But this allows to serialize writes and eliminate any possibility of conflict or logical errors during transaction rollback.
-
No WAL means relatively big WAF (Write Amplification Factor). Because of this syncing data to disk might be quite resource intensive and be main performance bottleneck during intensive write workload.
As compromise libmdbx allows several modes of lazy and/or periodic syncing, including
MAPASYNCmode, which modificate data in memory and asynchronously syncs data to disk, moment to sync is picked by OS.Although this should be used with care, synchronous transactions in a DB with transaction journal will require 2 IOPS minimum (probably 3-4 in practice) because of filesystem overhead, overhead depends on filesystem, not on record count or record size. In libmdbx IOPS count will grow logarithmically depending on record count in DB (height of B+ tree) and will require at least 2 IOPS per transaction too.
-
CoW for MVCC is done on memory page level with B+ trees. Therefore altering data requires to copy about Olog(N) memory pages, which uses memory bandwidth and is main performance bottleneck in
MAPASYNCmode.This is unavoidable, but isn't that bad. Syncing data to disk requires much more similar operations which will be done by OS, therefore this is noticeable only if data sync to persistent storage is fully disabled. libmdbx allows to safely save data to persistent storage with minimal performance overhead. If there is no need to save data to persistent storage then it's much more preferable to use
std::map. -
LMDB has a problem of long-time readers which degrades performance and bloats DB
libmdbx addresses that, details below.
-
LMDB is susceptible to DB corruption in
WRITEMAP+MAPASYNCmode. libmdbx inWRITEMAP+MAPASYNCguarantees DB integrity and consistency of data.Additionally there is an alternative:
UTTERLY_NOSYNCmode. Details below.
Long-time read transactions problem
Garbage collection problem exists in all databases one way or another (e.g. VACUUM in PostgreSQL). But in libmbdx and LMDB it's even more important because of high performance and deliberate simplification of internals with emphasis on performance.
-
Altering data during long read operation may exhaust available space on persistent storage.
-
If available space is exhausted then any attempt to update data results in
MAP_FULLerror until long read operation ends. -
Main examples of long readers is hot backup and debugging of client application which actively uses read transactions.
-
In LMDB this results in degraded performance of all operations of syncing data to persistent storage.
-
libmdbx has a mechanism which aborts such operations and
LIFO RECLAIMmode which addresses performance degradation.
Read operations operate only over snapshot of DB which is consistent on the moment when read transaction started. This snapshot doesn't change throughout the transaction but this leads to inability to reclaim the pages until read transaction ends.
In LMDB this leads to a problem that memory pages, allocated for operations during long read, will be used for operations and won't be reclaimed until DB process terminates. In LMDB they are used in FIFO manner, which causes increased page count and less chance of cache hit during I/O. In other words: one long-time reader can impact performance of all database until it'll be reopened.
libmdbx addresses the problem, details below. Illustrations to this problem can be found in the
presentation. There is also example of performance increase thanks to
BBWC when LIFO RECLAIM enabled in libmdbx.
Data safety in async-write mode
In WRITEMAP+MAPSYNC mode dirty pages are written to persistent storage by kernel. This means that in case of application
crash OS kernel will write all dirty data to disk and nothing will be lost. But in case of hardware malfunction or OS kernel
fatal error only some dirty data might be synced to disk, and there is high probability that pages with metadata saved,
will point to non-saved, hence non-existent, data pages. In such situation DB is completely corrupted and can't be
repaired even if there was full sync before the crash via `mdbx_env_sync().
libmdbx addresses this by fully reimplementing write path of data:
-
In
WRITEMAP+MAPSYNCmode meta-data pages aren't updated in place, instead their shadow copies are used and their updates are synced after data is flushed to disk. -
During transaction commit libmdbx marks synchronization points as steady or weak depending on how much synchronization needed between RAM and persistent storage, e.g. in
WRITEMAP+MAPSYNCcommited transactions are marked as weak, but during explicit data synchronization - as steady. -
libmdbx maintains three separate meta-pages instead of two. This allows to commit transaction with steady or weak synchronization point without losing two previous synchronization points (one of them can be steady, and second - weak). This allows to order weak and steady synchronization points in any order without losing consistency in case of system crash.
-
During DB open libmdbx rollbacks to the last steady synchronization point, this guarantees database integrity.
For data safety pages which form database snapshot with steady synchronization point must not be updated until next steady synchronization point. So last steady synchronization point creates "long-time read" effect. The only difference that in case of memory exhaustion the problem will be immediately addressed by flushing changes to persistent storage and forming new steady synchronization point.
So in async-write mode libmdbx will always use new pages until memory is exhausted or mdbx_env_sync()is invoked. Total
disk usage will be almost the same as in sync-write mode.
Current libmdbx gives a choice of safe async-write mode (default) and UTTERLY_NOSYNC mode which may result in full DB
corruption during system crash as with LMDB.
Next version of libmdbx will create steady synchronization points automatically in async-write mode.
Improvements over LMDB
-
LIFO RECLAIMmode:The newest pages are picked for reuse instead of the oldest. This allows to minimize reclaim loop and make it execution time independent from total page count.
This results in OS kernel cache mechanisms working with maximum efficiency. In case of using disk controllers or storages with BBWC this may greatly improve write performance.
-
OOM-KICKcallback.mdbx_env_set_oomfunc()allows to set a callback, which will be called in the event of memory exhausting during long-time read transaction. Callback will be invoked with PID and pthread_id of offending thread as parameters. Callback can do any of this things to remedy the problem:-
wait for read transaction to finish normally;
-
kill the offending process (signal 9), if separate process is doing long-time read;
-
abort or restart offending read transaction if it's running in sibling thread;
-
abort current write transaction with returning error code.
-
-
Guarantee of DB integrity in
WRITEMAP+MAPSYNCmode:
Current libmdbx gives a choice of safe async-write mode (default) and
UTTERLY_NOSYNCmode which may result in full DB corruption during system crash as with LMDB. For details see Data safety in async-write mode.
-
Automatic creation of synchronization points (flush changes to persistent storage) when changes reach set threshold (threshold can be set by
mdbx_env_set_syncbytes()). -
Ability to get how far current read-only snapshot is from latest version of the DB by
mdbx_txn_straggler(). -
mdbx_chktool for DB checking andmdbx_env_pgwalk()for page-walking all pages in DB. -
Control over debugging and receiving of debugging messages via
mdbx_setup_debug(). -
Ability to assign up to 3 markers to commiting transaction with
mdbx_canary_put()and then get them in read transaction bymdbx_canary_get(). -
Check if there is a row with data after current cursor position via
mdbx_cursor_eof(). -
Ability to explicitly request update of present record without creating new record. Implemented as
MDBX_CURRENTflag formdbx_put(). -
Ability to update or delete record and get previous value via
mdbx_replace()Also can update specific multi-value. -
Support for keys and values of zero length, including sorted duplicates.
-
Fixed
mdbx_cursor_count(), which returns correct count of duplicated for all table types and any cursor position. -
Ability to open DB in exclusive mode via
mdbx_env_open_ex(), e.g. for integrity check. -
Ability to close DB in "dirty" state (without data flush and creation of steady synchronization point) via
mdbx_env_close_ex(). -
Ability to get addition info, including number of the oldest snapshot of DB, which is used by one of the readers. Implemented via
mdbx_env_info(). -
mdbx_del()doesn't ignore additional argument (specifier)datafor tables without duplicates (without flagMDBX_DUPSORT), ifdatais not zero then always uses it to verify record, which is being deleted. -
Ability to open dbi-table with simultaneous setup of comparators for keys and values, via
mdbx_dbi_open_ex(). -
Ability to find out if key or value are in dirty page. This may be useful to make a decision to avoid excessive CoW before updates. Implemented via
mdbx_is_dirty(). -
Correct update of current record in
MDBX_CURRENTmode ofmdbx_cursor_put(), including sorted duplicated. -
All cursors in all read and write transactions can be reused by
mdbx_cursor_renew()and MUST be freed explicitly.
Caution, please pay attention!
This is the only change of API, which changes semantics of cursor management and can lead to memory leaks on misuse. This is a needed change as it eliminates ambiguity which helps to avoid such errors as:
- use-after-free;
- double-free;
- memory corruption and segfaults.
-
Additional error code
MDBX_EMULTIVAL, which is returned bymdbx_put()andmdbx_replace()in case is ambiguous update or delete. -
Ability to get value by key and duplicates count by
mdbx_get_ex(). -
Functions `mdbx_cursor_on_first() and mdbx_cursor_on_last(), which allows to know if cursor is currently on first or last position respectively.
-
If read transaction is aborted via
mdbx_txn_abort()ormdbx_txn_reset()then DBI-handles, which were opened in it, aren't closed or deleted. This allows to avoid several types of hard-to-debug errors. -
Sequence generation via
mdbx_dbi_sequence(). -
Advanced dynamic control over DB size, including ability to choose page size via
mdbx_env_set_geometry(), including on Windows. -
Three meta-pages instead two, this allows to guarantee consistently update weak sync-points without risking to corrupt last steady sync-point.
-
Automatic reclaim of freed pages to specific reserved space in the end of database file. This lowers amount of pages, loaded to memory, used in update/flush loop. In fact libmdbx constantly performs compactification of data, but doesn't use addition resources for that. Space reclaim of DB and setup of database geometry parameters also decreases size of the database on disk, including on Windows.
$ objdump -f -h -j .text libmdbx.so
libmdbx.so: file format elf64-x86-64
architecture: i386:x86-64, flags 0x00000150:
HAS_SYMS, DYNAMIC, D_PAGED
start address 0x000030e0
Sections:
Idx Name Size VMA LMA File off Algn
11 .text 00014d84 00000000000030e0 00000000000030e0 000030e0 2**4
CONTENTS, ALLOC, LOAD, READONLY, CODE
$ gcc -v
Using built-in specs.
COLLECT_GCC=gcc
COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/7/lto-wrapper
OFFLOAD_TARGET_NAMES=nvptx-none
OFFLOAD_TARGET_DEFAULT=1
Target: x86_64-linux-gnu
Configured with: ../src/configure -v --with-pkgversion='Ubuntu 7.2.0-8ubuntu3' --with-bugurl=file:///usr/share/doc/gcc-7/README.Bugs --enable-languages=c,ada,c++,go,brig,d,fortran,objc,obj-c++ --prefix=/usr --with-gcc-major-version-only --program-suffix=-7 --program-prefix=x86_64-linux-gnu- --enable-shared --enable-linker-build-id --libexecdir=/usr/lib --without-included-gettext --enable-threads=posix --libdir=/usr/lib --enable-nls --with-sysroot=/ --enable-clocale=gnu --enable-libstdcxx-debug --enable-libstdcxx-time=yes --with-default-libstdcxx-abi=new --enable-gnu-unique-object --disable-vtable-verify --enable-libmpx --enable-plugin --enable-default-pie --with-system-zlib --with-target-system-zlib --enable-objc-gc=auto --enable-multiarch --disable-werror --with-arch-32=i686 --with-abi=m64 --with-multilib-list=m32,m64,mx32 --enable-multilib --with-tune=generic --enable-offload-targets=nvptx-none --without-cuda-driver --enable-checking=release --build=x86_64-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-linux-gnu --target=x86_64-linux-gnu
Thread model: posix
gcc version 7.2.0 (Ubuntu 7.2.0-8ubuntu3)